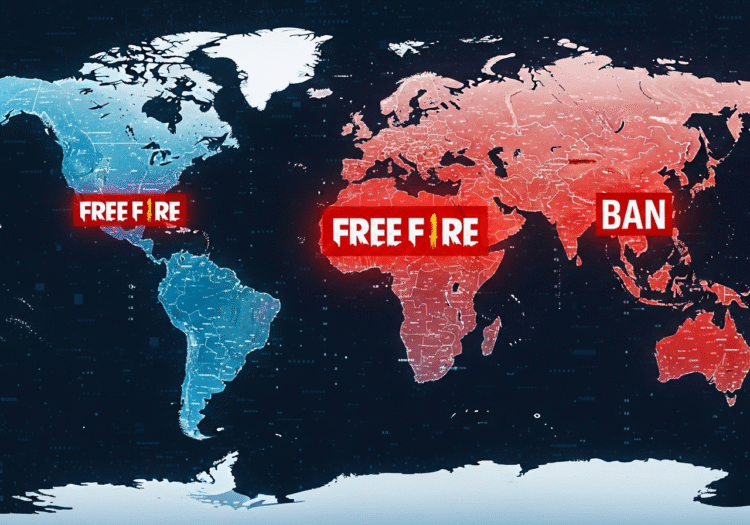
For many mobile gamers, Free Fire has been a go-to battle royale experience. It’s known for running well on many devices, its quick matches, and engaging gameplay. However, if you’ve been following gaming news, you might have noticed a pattern: mentions of Free Fire being banned or facing tough scrutiny in various countries. Even with recent exciting news like the Free Fire Max India Cup 2025 tournament, the underlying concerns that led to past bans haven’t completely disappeared in the global landscape.
So, why do these bans happen? Is it a global trend, or are there specific reasons? Let’s explore the ongoing challenges and factors that lead countries to restrict popular mobile games like Free Fire.
1. The Rollercoaster: Free Fire’s Global Presence and Past Bans
Free Fire, developed by Garena, quickly became one of the most downloaded mobile games worldwide. Its simple mechanics and accessibility made it a hit, especially in emerging markets. Yet, this popularity has also placed it under a magnifying glass. While it enjoys massive player bases in regions like Southeast Asia and Latin America, it has also faced significant hurdles, including outright bans. India, for instance, famously banned the game in 2022, though Free Fire Max has recently seen a partial return for esports, which we’ll discuss. This mixed global reception shows that a game’s success isn’t just about its popularity, but also about navigating complex national rules and concerns.
2. Key Reasons Behind Game Bans: It’s More Than Just Gameplay
When a country decides to ban a popular game, it’s rarely just about the game itself being “too violent” or “too addictive.” While those aspects can play a part, the deeper reasons often involve national security, data handling, and local competition.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
This is often the leading reason for bans, especially in recent years. Governments are becoming increasingly strict about how user data is collected, stored, and shared. They worry about:
- Unauthorized Data Collection: Whether the game collects more personal data than is necessary or without clear consent.
- Server Locations: Where user data is stored. If data is routed to servers in countries with less strict data protection laws or to countries considered a security risk, it raises red flags.
- Links to Foreign Entities: If a game developer or its parent company has strong ties to a specific foreign government, there can be concerns about potential access to sensitive user data by that government.
For Free Fire, despite Garena being a Singaporean company, past bans (like in India) specifically cited worries about data security and links that could pose national security threats. This concern isn’t unique to Free Fire; many apps from various origins have faced similar scrutiny.
Links to Specific Countries or Companies
In a world where digital security is paramount, governments are increasingly cautious about apps developed or owned by companies with ties to nations perceived as geopolitical rivals or having questionable data practices. Even if the game itself is popular, its origin or ownership structure can become a point of contention, leading to a ban not because of the game’s features, but because of who controls its data flow.
Addiction and Mental Health Worries
While less common as a direct legal reason for an outright ban, concerns about excessive screen time and gaming addiction do influence public opinion and can add pressure on governments. Some countries might introduce stricter playtime limits or parental controls, rather than a full ban, but severe public health concerns could contribute to a broader regulatory push.
Content Suitability and Cultural Norms
In some regions, games might face restrictions due to their content if it’s deemed to violate local cultural, religious, or moral standards. This could involve themes of violence, certain in-game items, or even character designs. While battle royale games generally involve combat, the specific art style or thematic elements in Free Fire could potentially draw attention in culturally conservative nations.
Competition and Local Regulations
Sometimes, a ban isn’t purely about security. It could also be influenced by a desire to promote local game developers or to ensure that foreign companies comply with specific local business or content regulations that are difficult to meet. While less direct, a strong local gaming industry might subtly influence policy decisions.
3. The India Case: A Clear Example of Free Fire’s Ban and Return (for Max)
India offers a very public example of the complexities surrounding Free Fire’s regulatory journey.
The 2022 Ban: National Security and Data
In February 2022, the original Garena Free Fire was banned in India alongside dozens of other apps, primarily those with perceived links to China. The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) cited Section 69A of the IT Act, pointing to concerns over “unauthorized data collection of Indian users,” “possible links to Chinese servers,” and “threats to national security.” Despite Garena’s Singaporean base, these concerns were enough to remove the game from both the Google Play Store and Apple App Store in India.
The Free Fire Max Tournament 2025: A Nuanced Comeback
Interestingly, in July 2025, Garena announced the “TEZ Free Fire Max India Cup 2025” esports tournament, marking a major return to the Indian competitive scene. This event is being played exclusively on Free Fire Max, the enhanced version of the game that was not part of the initial 2022 ban. This suggests a careful strategy by Garena to re-engage with the Indian market by leveraging the version of the game that remained operational and potentially complies better with local rules. While the original Free Fire remains inaccessible in India, the tournament indicates a strategic pathway for Garena to operate in a regulated environment. This shows that bans aren’t always permanent or absolute; sometimes, a company can adapt to meet a country’s specific demands, often related to data localization or company structure.
4. Beyond India: Are Other Countries Following Suit?
While India’s ban on the original Free Fire was a high-profile case, it set a precedent. Other countries, particularly those with similar geopolitical concerns or growing digital sovereignty movements, are likely watching closely. As of mid-2025, there haven’t been widespread new specific bans on Free Fire announced in multiple other countries. However, the general trend of increased scrutiny on foreign apps, especially concerning data privacy and national security, continues globally.
This means that while Free Fire might not be “getting banned in more countries” every week, it (and other global apps) constantly operates under the risk of new regulations or bans if it fails to meet a country’s evolving digital safety standards. The concerns that led to India’s ban are global issues, and any nation could implement similar restrictions if it deems necessary.
5. What This Means for Players and Garena
For players in countries where Free Fire (or Free Fire Max) is banned, it means finding alternative games or, in some cases, using unofficial and often risky methods like VPNs or unofficial APKs to access the game. These unofficial methods come with their dangers, including security risks like malware or potential account bans from Garena itself if they violate the terms of service.
For Garena, it means a continuous effort to comply with diverse and evolving national regulations. This includes:
- Data Localization: Storing user data within the country where users reside.
- Transparent Data Practices: Being very clear about what data is collected and why.
- Local Partnerships: Collaborating with local companies or setting up local subsidiaries to build trust.
- Version Differentiation: Offering specific versions of the game (like Free Fire Max) that meet local requirements.
6. Looking Ahead: The Future of Free Fire and Mobile Gaming Regulations
The trend of countries taking a stronger stance on data privacy and digital sovereignty is not going away. For global games like Free Fire, this means a future where adapting to local laws and concerns is just as important as creating engaging gameplay. The Free Fire Max India Cup 2025 highlights Garena’s strategy to navigate these complex waters by offering a compliant version and focusing on local engagement.
While there might not be a sweeping wave of new bans happening every day, the reasons behind past bans – especially data security and national concerns – remain active considerations for governments worldwide. The ability of Free Fire, and indeed any global app, to continue operating widely will depend on its proactive measures to meet these stringent national requirements and build trust with regulators. The battle for global popularity now includes a crucial fight for regulatory compliance.